Unit: AM/FM Stereo Receiver
Manufacturer: JVC
Model: VR-5551
SN: 13402565
A pretty rare JVC VR-5551 stereo receiver is on my bench today. This model was manufactured from 1972 to 1975 and held the top position in JVC's production line, featuring the VR-5551, VR-5541, VR-5521, VR-5511, and VR-5501. It delivers 50 watts per channel into 8 ohms with no more than 0.5% total harmonic distortion. The damping factor at 8 ohm is 50. The retail price in 1972 was approximately $450.
An interesting feature of this model is the five-band version of the Sound Effects Amplifier (U.S. Patent No. 3,566,294 issued February 1971). The five sliders are calibrated to boost or cut up to 12dB over frequency bands with center reference frequencies of 40Hz, 250Hz, 1kHz, 5kHz, and 15kHz, respectively. These sliders operate continuously, registering clicks every 2 dB on the scale. Below the SEA section are six pushbuttons for FM muting, loudness, mono mode, low filter, high filter, and SEA defeat.
The other features of the VR-5551 are a black face dial with a "Bull's eye" FM dial pointer, two tuning meters, front-panel tape recording & playback jacks for recording with or without SEA, left and right microphone inputs with their own master level control, a special protector circuit, and a luxurious walnut wooden cabinet.
The VR-5551 receiver is easy to service, with the exception of two double-soldered PCBs, to which access is restricted.
Power Supply Board (TAP-113)
The power supply board has 7 aluminum electrolytic capacitors: C801, C802, C804, C806, C807, C808, and C810. All of them were replaced with low impedance Nichicon UPW/UPM caps. The old glue around some large e-caps was carefully removed. This glue often corrodes capacitor leads and even can damage the PCB. I highly recommend removing it before installing new capacitors.
The original e-caps were tested with an Atlas ESR70 capacitance meter; the results are below.
Test results on original capacitors removed from the power supply board:
C801: rated capacitance – 470uF, measured – 497uF, ESR – 0.05Ω, deviation: +6%
C802: rated capacitance – 470uF, measured – 494uF, ESR – 0.06Ω, deviation: +5%
C804: rated capacitance – 470uF, measured – 576uF, ESR – 0.03Ω, deviation: +23%
C806: rated capacitance – 470uF, measured – 576uF, ESR – 0.05Ω, deviation: +23%
C807: rated capacitance – 470uF, measured – 591uF, ESR – 0.07Ω, deviation: +26%
C808: rated capacitance – 220uF, measured – 245uF, ESR – 0.12Ω, deviation: +11%
C810: rated capacitance – 470uF, measured – 580uF, ESR – 0.12Ω, deviation: +23%
Power supply board - before and after
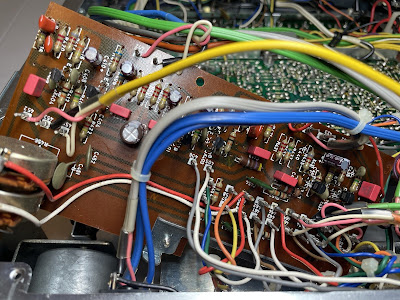
Driver Amplifier Board (TAD-79)
The driver amplifier board is fixed in a slot which greatly simplifies the servicing of this board. It has one axial (C719) and 12 radial (C701, C702, C703, C704, C707, C708, C709, C710, C711, C712, C718) aluminum electrolytic capacitors. The e-caps C701 and C702 installed in the input signal path were replaced with high-quality film polyester WIMA caps. Other two e-caps C703 and C704 installed in the signal path were replaced with modern low leakage Nichicon UKL caps. The original axial capacitor C719 was replaced with a Vishay axial e-cap (500D series). And the remaining aluminum e-caps were replaced with low impedance Nichicon UPW/UPM caps.
Test results on original capacitors removed from the driver amplifier board:
C701: rated capacitance – 1uF, measured – 1.3uF, ESR – 1.32Ω, deviation: +30%
C702: rated capacitance – 1uF, measured – 1.2uF, ESR – 1.31Ω, deviation: +20%
C703: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 40uF, ESR – 0.45Ω, deviation: +21%
C704: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 40uF, ESR – 0.49Ω, deviation: +21%
C707: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 119uF, ESR – 0.22Ω, deviation: +19%
C708: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 113uF, ESR – 0.24Ω, deviation: +13%
C709: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 126uF, ESR – 0.89Ω, deviation: +26%
C710: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 131uF, ESR – 0.21Ω, deviation: +31%
C711: rated capacitance – 47uF, measured – 57uF, ESR – 1.22Ω, deviation: +21%
C712: rated capacitance – 47uF, measured – 58uF, ESR – 0.59Ω, deviation: +23%
C717: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 119uF, ESR – 0.13Ω, deviation: +19%
C718: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 116uF, ESR – 0.14Ω, deviation: +16%
C719: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 1.58Ω, deviation: +20%
The prone-to-failure Hitachi 2SC458LG transistor installed in positions X701, X702, X709, X710, X711, and X712 was replaced with a low-noise Fairchild KSC1845 transistor. Watch the pinout on replacement transistors. The original transistor is BCE and the new one is ECB.
Driver amplifier board - before and after
Equalizer Circuit Board (TAE-47)
The equalizer circuit board is also fixed in a separate slot. This board has 11 aluminum electrolytic capacitors: C501, C502, C503, C504, C507, C508, C511, C512, C513, C514, and C521. All e-caps installed in the signal path (C501, C502, C507, C508, C511, C512) were replaced with modern low leakage Nichicon UKL caps to reduce the noise generated in the circuit. The remaining aluminum e-caps were replaced with low impedance Nichicon UPW caps.
Test results on original capacitors removed from the equalizer circuit board:
C501: rated capacitance – 3.3uF, measured – 3.6uF, ESR – 1.1Ω, deviation: +9%
C502: rated capacitance – 3.3uF, measured – 3.5uF, ESR – 0.59Ω, deviation: +6%
C503: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 13uF, ESR – 1.65Ω, deviation: +30%
C504: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 13uF, ESR – 1.71Ω, deviation: +30%
C507: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 0.78Ω, deviation: +20%
C508: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 0.77Ω, deviation: +20%
C511: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 0.56Ω, deviation: +20%
C512: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 0.68Ω, deviation: +20%
C513: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 120uF, ESR – 0.27Ω, deviation: +20%
C514: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 115uF, ESR – 0.26Ω, deviation: +15%
C521: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 11uF, ESR – 0.72Ω, deviation: +10%
All notorious Hitachi 2SC458LG transistors installed in positions X501 thru X504 were replaced with low-noise Fairchild KSC1845 transistors. Again, watch the pinout on replacement transistors. The original transistor is BCE and the new one is ECB.
Equalizer circuit board - before and after
SEA Circuit Board (TAC-147)
The SEA circuit board in this receiver is a double-soldered PCB. This type of PCB is very difficult to service especially if the other side is not accessible. Fortunately, this board has only 4 electrolytic capacitors to be replaced: C621, C522, C623, and C624. I replaced two e-caps with a nominal capacitance of 0.62uF with film polyester WIMA caps. The other two e-caps were replaced with low leakage Nichicon UKL caps.
Test results on original capacitors removed from the SEA circuit board:
C621: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 0.34Ω, deviation: +20%
C622: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 11uF, ESR – 0.68Ω, deviation: +10%
C623: rated capacitance – 0.68uF, measured – 0.66uF, ESR – N/A, deviation: -3%
C624: rated capacitance – 0.68uF, measured – 0.62uF, ESR – N/A, deviation: -9%
SEA circuit board - before and after
Microphone Amplifier Board (TAC-150)
The microphone amplifier board has 7 aluminum electrolytic capacitors: C661, C662, C663, C664, C665, C666, and C671. I replaced two e-caps (C661 & C662) installed in the input signal path with film polyester WIMA caps. All other e-caps were replaced with low impedance Nichicon UPW capacitors.
Test results on original capacitors removed from the microphone amplifier board:
C661: rated capacitance – 1uF, measured – 1.4uF, ESR – 1.24Ω, deviation: +40%
C662: rated capacitance – 1uF, measured – 1.3uF, ESR – 1.34Ω, deviation: +30%
C663: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 13uF, ESR – 1.42Ω, deviation: +30%
C664: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 13uF, ESR – 1.53Ω, deviation: +30%
C665: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 119uF, ESR – 0.42Ω, deviation: +19%
C666: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured – 111uF, ESR – 0.26Ω, deviation: +11%
C671: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 1.22Ω, deviation: +20%
This board also has 4 notorious Hitachi 2SC458LG transistors installed in positions X651 thru X654. I replaced them with low-noise Fairchild KSC1845 transistors. Again, watch the pinout on replacement transistors. The original transistor is BCE and the new one is ECB.
Microphone amplifier board - before and after
Switch Assembly (TAC-148)
The switch assembly is another double-soldered PCB in this receiver. I recommend removing this board from the chassis before servicing. Otherwise, there is a high probability of burning the dial cord behind this board.
The switch assembly has 11 aluminum electrolytic capacitors: C605, C606, C607, C608, C609, C610, C611, C612, C613, C614, and C619. I replaced two e-caps (C605 & C606) installed in the input signal path with film polyester WIMA caps. The other e-caps (C607, C608, C611, C612) installed in the signal path were replaced with modern low leakage Nichicon UKL caps. And the remaining aluminum e-caps were replaced with low impedance Nichicon UPW caps.
Test results on original capacitors removed from the switch assembly:
C605: rated capacitance – 1uF, measured – 1.2uF, ESR – 2.1Ω, deviation: +20%
C606: rated capacitance – 1uF, measured – 1.2uF, ESR – 2.2Ω, deviation: +20%
C607: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 42uF, ESR – 0.72Ω, deviation: +27%
C608: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 40uF, ESR – 0.92Ω, deviation: +21%
C609: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 0.64Ω, deviation: +20%
C610: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 0.98Ω, deviation: +20%
C611: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 39uF, ESR – 0.43Ω, deviation: +18%
C612: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 38uF, ESR – 0.56Ω, deviation: +15%
C613: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 38uF, ESR – 2.6Ω, deviation: +15%
C614: rated capacitance – 33uF, measured – 38uF, ESR – 2.4Ω, deviation: +15%
C619: rated capacitance – 10uF, measured – 12uF, ESR – 1.1Ω, deviation: +20%
Switch assembly - before and after
Main Filter and Two Coupling Capacitors
The original filter capacitor in this unit was replaced with a new Kemet screw terminal electrolytic capacitor. Additionally, the original coupling capacitors were replaced with Nichicon LKG capacitors. The LKG series was specifically designed for high-grade audio equipment and, in my opinion, is the best replacement option for the original filter and/or coupling capacitors available on the market. The new Nichicon LKG e-caps have the same diameter as the original ones but are shorter in length. As a result, the same clamps can be used to attach them to the chassis.
Test results on the original filter and coupling capacitors:
C4: rated capacitance – 2200uF, measured – 2782uF, ESR – 0.08Ω, deviation: +27%
C4: rated capacitance – 2200uF, measured – 2380uF, ESR – 0.07Ω, deviation: +8%
C5: rated capacitance – 2200uF, measured – 2417uF, ESR – 0.07Ω, deviation: +10%
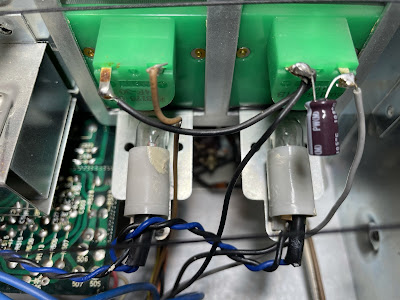
Dial and Meter Lamps
The dial and meter lamps in this model are easily accessible. I replaced them with new incandescent lamps (screw base, 300mA, 8V).
The Stereo indicator lamp was also replaced with a new incandescent lamp (4mm, 40mA, 6V).
Dial lamps - screw base
Meter lamps - screw base
Center Voltage and Idling Current Adjustments
There is some confusion in the service manual regarding the adjustment of the center voltage and idling current. The service manual states that the center voltage on each channel must be adjusted with a trimming resistor R102, as shown in the circuit on page 9. Additionally, the idling current should be adjusted using a trimming resistor R101, also detailed in the circuit on the same page. However, the schematic diagram displays these trimming resistors as R719/R720 (center voltage) and R735/R736 (idling current). Furthermore, the driver amplifier board being serviced lacks trimming resistors R735 and R736 to adjust the idling current. Instead, two resistors (with a nominal resistance of 8.2Ω each) were factory soldered in positions R735 and R736. This makes the adjustment of the idling current problematic in this unit. It appears that JVC implemented this as a cost-reduction solution during the production of this model.
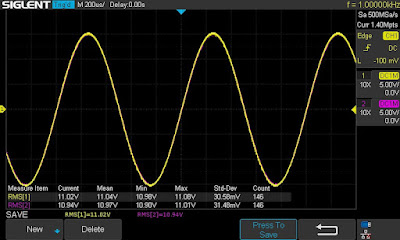
To adjust the center voltage on each channel, it must be set to half of the +B1 voltage. The +B1 voltage can be measured between pin #6 on the driver amplifier board and the ground (or across the main filter capacitor). In this unit, the measured +B1 voltage was 84.1 DC. The center voltage is measured between the positive lead of coupling capacitor C4/C5 (2200uF/63V) and the ground. I adjusted the center voltage on each channel to half of the measured +B1 voltage using trimming resistors R719/R720.
According to the service manual, the idling current on each channel must be between 10mA to 20mA. The idling current can be calculated by measuring the voltage drop across the emitter resistor R5 (R6). Since the nominal resistance of R5 (R6) is 0.5Ω, the voltage drop across each resistor should be between 5mV to 10mV. I measured the voltage drop across emitter resistor R5 (left channel), and it was close to ~11mV. However, the measured voltage drop across emitter resistor R6 (right channel) was close to ~32mV, which is about three times higher than the recommended value in the manual. As I mentioned earlier, this particular unit has no trimming resistor to adjust the idling current. So, the only way to adjust it is to replace the single resistor factory soldered in position R736. I replaced it with a KOA Speer metal film resistor with a nominal resistance of 3.32Ω, and it reduced the idling current on the right channel to ~16mA (the measured voltage drop across R736 is ~8mV).
+B1 voltage measured between pin #6 and ground
The center voltage on the left and right channels after restoration
Bias on the left and right channels after restoration
Output Power Test
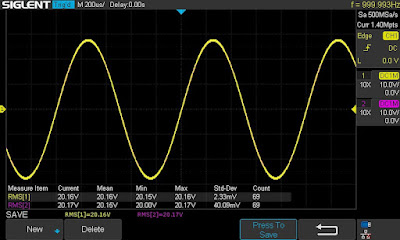
The final output power test was performed at the end of my restoration. The receiver was loaded with a low inductance 8Ω/100W dummy resistor for each channel. The oscilloscope was connected across the speaker terminals and a sine-wave signal of 1kHz was applied to the AUX jacks. The output sine-wave signal was perfectly symmetrical on both channels with no clipping up to 20.16 VRMS (left channel) and 20.17 VRMS (right channel). It corresponds to the output power of 50.8W on the left channel and 50.9W on the right channel.
Output power test
As usual, all the knobs and the front panel were gently cleaned in warm water with dish soap. All controls have been cleaned with DeoxIT 5% contact cleaner and lubricated with DeoxIT FaderLube 5% spray.
The final result can be seen in the photos below. This model looks and sounds awesome! Please watch a short demo video at the end of this post. Thank you for reading.
JVC VR-5551 - after restoration


_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)
_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)
_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)
_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)
_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)
_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)